My life was lived out of reaction to what other people did, or might do or what they thought or might think about me
Peter Scazzero
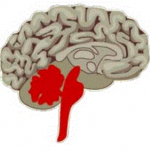
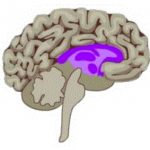
This comes from the triune brain theory. They different parts of our brain evolved at different stages and drive our reactions (Paul Mclean)
| Lizard brain | Mammal Brain | Human Brain |
 |
 |
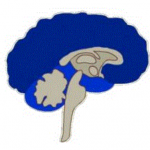 |
| Brain stems & cerebellum | Limbic System | Neocortex |
| Fight or Flight | Emotions, memories, habits | Language, abstract thought, imagination, consciousness |
| Autopilot | Decisions | Reasons, rationalises |
These three types of ‘limbic’ responses are often followed by pacifying behaviours, which are representative of the brain directing the body to provide comforting actions in order to calm down and restore normal conditions. By observing these pacifying behaviours, you can detect when someone has reacted negatively to some situation – perhaps something you have said or done.
Examples of pacifying behaviours:
- Covering the neck, such as playing with a necklace or adjusting a tie
- Rubbing your forehead
- Touching or rubbing your neck
- Touching or rubbing your cheek
- Exhaling with your cheeks puffed out
- The “leg cleanser” – when sitting, pushing your hands from the top of your legs toward your knees
- The “ventilator” – pulling on your shirt collar (for men) or tossing the back of your hair up (for women) These are reactions. A response is the opposite to a reaction.
It is a refusal to run away from difficulties or any part of your life or reality that you happen to dislike. When you take full ownership of your life in this way, you gain confidence and momentum in making good decisions. (Danny Silk)
(Source Wendy Behary, Disarming the Narcissist & Joe Navarro, What every BODY is saying)
We have 3 typical reactions to bad news:
| Freeze | Flight | Fight |
| |
|
|
| Do nothing. Try to ignore it or stop making decisions | Try to get away from the pain (avoid it) | Push back with counterattack |
|
|
o Puffing out your chest
o Violating personal space o Aggressive posture |
| “You’re right; it’s all my fault” | The more you avoid, the more your opponent pursues, demands, and persists. You end up feeling cornered and incapacitated | “I’ll show you” |
| “It seems that you are upset with me, and when I sense that I have a tendency to give up and give in. I know that this makes you more upset, but that isn’t my intention.” | “I know this issue is important to you. It’s also important to me, but I’m feeling flooded right now. I need some time alone to regroup and gather my thoughts, so our conversation might be productive.” | “I won’t tolerate being treated so disrespectfully. If you’re uncomfortable with me, you can tell me without putting me down or ignoring me. I’d appreciate it if you could speak to me with more consideration and I’ll do the same for you.” |